Titanium dioxide and its effects on Human gut health
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is an inorganic compound that occurs naturally, and it is very common additive in foods, medicines and grooming products because of its whitening properties. It is also known as titanium (IV) oxide or titania and when used as a pigment, its often-called titanium white, Pigment White 6, or CI 77891. It is added as a food additive (E171) as a white pigment in various foodstuffs to make food appear brighter and more appealing. It is used in food such as candies, chewing gums, coffee creamer, cake decorations, and white sauces. In medicine it is used as pigment, coating, and packaging material to enhance its opacity and to protect its photosensitive substances.
The Human gut is a very complex ecosystem which is home to billions or trillions of microorganisms collectively known as gut microbiota. Human gut plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, immune system development and enhancement, and even mental health. A healthy and balanced gut microbiome is fundamental for overall well- being. But what happens when an additive like titanium dioxide which seems like a harmless additive enters into this delicate and important part of human body?

The Nanoparticle Question?
One thing that makes it hard to say that if titanium dioxide is safe, is its size. It is present in both micro and nano-sized forms. TiO2 (E171) is most of what we find in food. Yet, a good chunk of it (30%, 40%) might be in nanoparticles with diameters less than 100 nanometres. This distinction is critical because nanoparticles behave differently in human body. Due to their extremely small size, they have a large outer area to their size, allowing them to break down or dissolve faster and, crucially, to more easily penetrate cells and tissues. This enhanced bioavailability and potential for accumulation within the body are the major emerging concern.
Disrupting the Gut Barrier:
The intestinal or gut barrier is a sophisticated defense system that prevents harmful substances, toxins and unwanted microbes from entering the bloodstream while allowing only essential and healthy nutrients to pass through. It is a single layer of epithelial cells, sealed tightly by “tight junctions” and protected by a thick mucus layer, a home to many beneficial bacteria.
Studies suggest that titanium dioxide, particularly in its nano form, can compromise this vital barrier. Research has shown that TiO2 can:
-
Reduce mucus production and alter its composition:
The mucus layer acts as a physical and chemical shield. TiO2 exposure has been linked to reduction in the mucin 2 (MUC2) gene which is a key component of the intestinal mucus and even the absorption of mucin protein itself. A thinner and compromised mucus layer makes the epithelial cells more vulnerable to bacteria.
-
Increase intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”):
By affecting tight junction proteins, TiO2 can essentially create “gaps” in the intestinal lining, allowing substances that should remain in gut lumen to leak into the bloodstream. This “leaky gut” phenomenon is a known and main contributor to chronic inflammation and various health issues.
-
Direct impact on intestinal cells:
In vitro studies using human intestinal epithelial cells (like Caco-2 cells) have shown that TiO2 can reduce cell creation, impair metabolic activity, and even induce the release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), a marker of cell damage, especially if left long exposed.
Gut-Liver Axis impact
The gut-liver axis is a crucial bidirectional communication pathway between the gastrointestinal tract (gut) and the liver. It involves the interplay of gut microbiota, their metabolites, the intestinal barrier, and immune signals that influence liver health and function. Absorption of TiO2 can affect the gut-liver axis, potentially influencing liver health through changes in bile acid metabolism. It can cause:
-
Dysbiosis and its Consequences:
Other than the physical barrier, TiO2 has been observed to significantly alter the composition the function of the gut microbiota, leading to a state known as dysbiosis. TiO2 can alter the composition and function of the gut microbiota, leading to dysbiosis. It can decrease beneficial bacteria and their production of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are crucial for maintaining gut barrier integrity. It can also increase pro-inflammatory bacteria or their metabolites.
-
Increased Toxin Translocation to the liver:
With a “leaky gut” and dysbiotic microbiota, more bacterial products and toxins, particularly LPS, can translocate from the gut to the liver via the portal vein. The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, and it is the first organ to receive blood from the gut. When constantly exposed to an increased load of toxins, the liver can become overwhelmed.
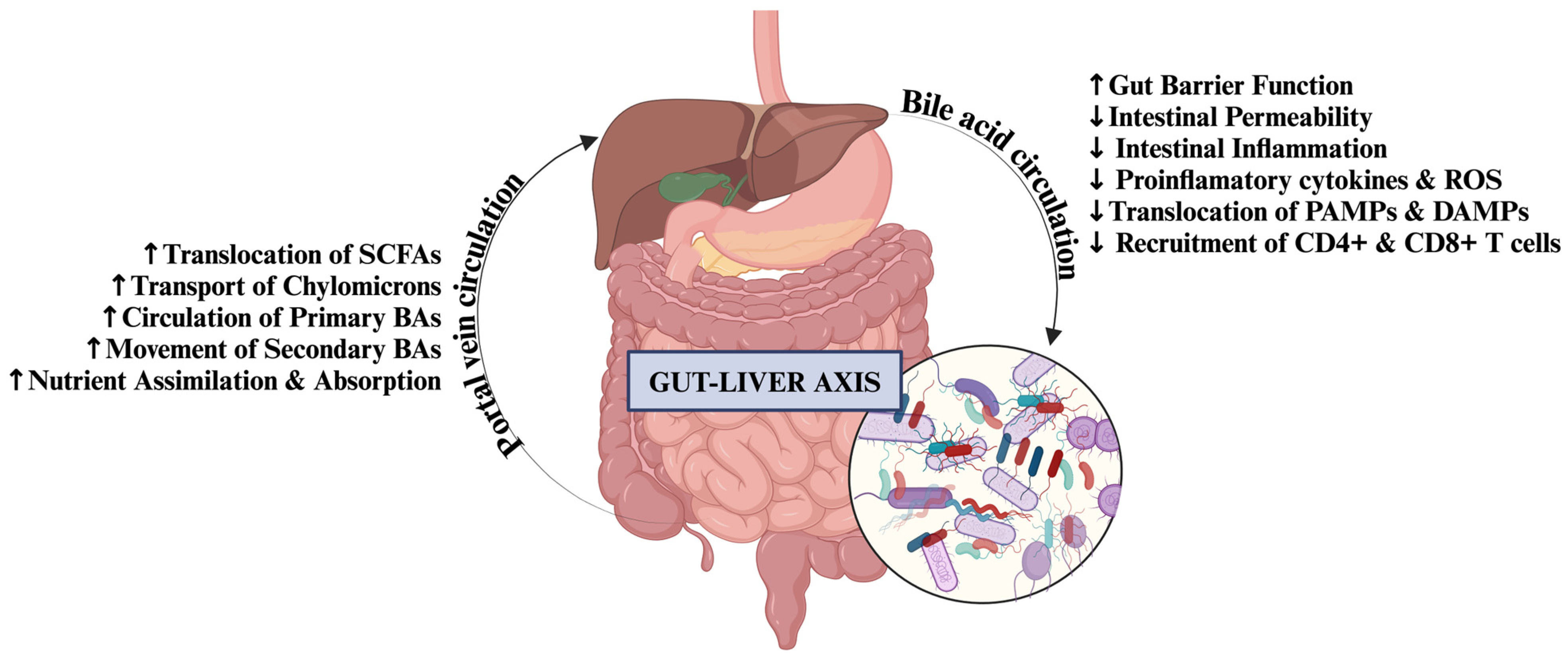
Liver Inflammation and Oxidative Stress:
Once reached in the liver, these gut-derived toxins and even absorbed TiO2 nanoparticles themselves can trigger an inflammatory response. TiO2 has been shown to induce oxidative stress and inflammation in liver cells, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This can cause severe liver cell damage and elevate liver enzymes like AST and ALT. Chronic low-grade inflammation driven by the gut-liver axis is a key factor in the development and progression of various liver diseases, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and more severe conditions like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Immune System Effects:
When titanium dioxide (TiO2) particles, particularly nanoparticles, are absorbed into the bloodstream from the gut, they can interact with various components of the immune system throughout the body. The chronic low-grade inflammation initiated in the gut due to TiO2 exposure, coupled with the direct immune activation and oxidative stress after systematic absorption, could contribute to a state of chronic systematic inflammation.
This systematic inflammation is a known risk factor for various non-communicable diseases, including metabolic disorders and potentially autoimmune or aggravation of autoimmune diseases is still limited and requires more research.
Human Studies:
The long-term human studies on dietary TiO2 and its specific role in the development or aggravation of inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD) are still emerging and somewhat limited, especially when compared to the wealth of animal and in vitro data.
Key findings from human studies:
-
Presence in IBD Patients Blood:
One of the most significant human findings comes from study by Ruiz et al. (2017), which demonstrated increased levels of titanium in the blood of patients with active ulcerative colitis (UC). This is a very crucial piece of evidence, as it suggests that in individuals with a compromised intestinal barrier (common in IBD). TiO2 can indeed translocate from the gut into the systemic circulation. This finding supports the “leaky gut” hypothesis and indicates that TiO2 is not merely passing through the digestive system.
-
In Vitro Human Cell Responses:
Numerous studies using human intestinal epithelial cell lines (like Caco-2) and human macrophages have consistently shown that TiO2 (both nano and micro forms) can:
- Be internalized by these cells.
- Induce oxidative stress
- Trigger inflammatory responses
- Increase intestinal permeability
- Cause cell damage at higher concentrations or with prolonged exposure.
Dose Dependent Effects
Most studies (animal and in vitro) show that the adverse effects of TiO2 (gut barrier disruption, inflammation, microbial shifts) become more pronounced with higher doses. This is a fundamental principal of toxicology.
Conclusion
While titanium dioxide (E171) has long been used in food and personal care products for its whitening properties, emerging research raises concerns about its potential impact on gut health. Studies suggest that consistent exposure may disrupt gut microbiota balance, impair intestinal barriers, and trigger inflammation, especially in individuals with pre-existing gut issues. As scientific understanding continues to evolve, it’s essential for consumers to stay informed and for regulatory bodies to reevaluate the safety of such additives. Prioritizing whole, minimally processed foods remains a proactive step toward maintaining a healthy gut.
The post Titanium Dioxide Effects on Gut Health appeared first on Medifyhome.





