Healthcare systems worldwide are experiencing a significant increase in the adoption of AI in healthcare. These intelligent systems can analyze a patient’s symptoms, review medical history, and provide treatment options in minutes. Although AI is set to revolutionize healthcare, many patients and professionals still have difficulties trusting it. Even studies found that people from different backgrounds, including younger and tech-savvy professionals, can be skeptical about using AI technology in healthcare.
Because of this lack of trust, healthcare innovation that could help people and improve results is being blocked. By 2025, healthcare organizations must handle this skepticism to improve the adoption of new medical technologies. Building trust among patients and healthcare providers is as important as the development of new AI healthcare solutions.
Data is now the main factor in overcoming this trust issue by showing how AI can be dependable, clear and useful in healthcare settings.
The Skepticism Surrounding AI in Healthcare
1. Patient Concerns
Healthcare consumers are hesitant about using AI in medical applications, which slows down its adoption rates. A recent survey by the Pew Research Centre indicates that around 60% of Americans prefer their healthcare provider to avoid using AI for medical decisions. Patients object to this for several reasons, including the fear of losing personal touch in healthcare.
Traditionally, patients value empathy from doctors, and they worry that AI in healthcare will take away the compassion in care. According to a survey, 53% of people in the US believe AI cannot serve as an effective alternative to human health specialist,s and 43% prefer to interact with a person during their healthcare.
2. Provider Hesitancy
Medical staff and healthcare providers tend to have similar doubts about implementing artificial intelligence in hospitals. Many providers are hesitant because they are unsure about how accurate and reliable AI systems are. Medical experts need assurance that these technologies will benefit patients and not introduce new dangers. Healthcare providers express specific concerns about AI implementation:
- 89% of physicians demand vendor transparency about data gathering, creation, and usage
- Many staff members worry about job security as AI integration advances
The Cost of Distrust
Widespread skepticism creates measurable impacts on healthcare systems and patient care quality. If healthcare providers are slow to adopt AI or patients decline AI-assisted testing, the healthcare system will miss out on better care and efficiency. Failing to use AI leads to slower diagnosis, fewer choices for precise treatment and higher inefficiency in operations. Healthcare leaders are aware of the benefits; 92% mention them for efficiency and 65% for making decisions faster.
However, these challenges present opportunities for improvement.
The Role of Data in Building Trust
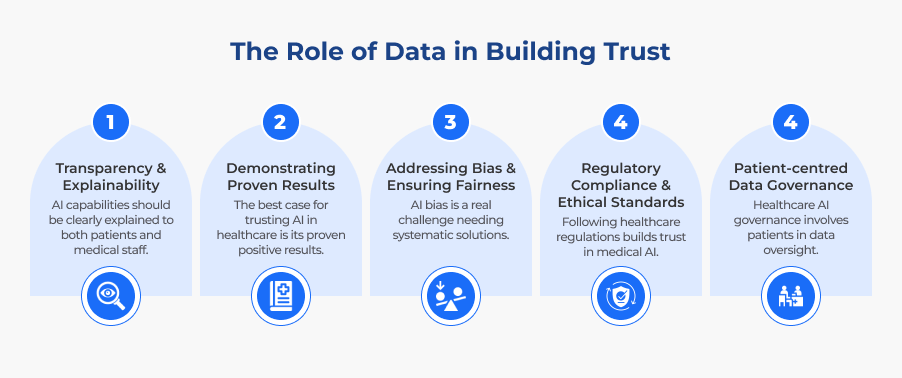
1. Transparency and Explainability
AI systems being “black box” nature makes it difficult for users in healthcare to trust them. More transparency is needed in artificial intelligence healthcare applications to help users understand operational mechanisms.
AI capabilities should be explained clearly so that patients and medical staff can both understand them. When open data access policies are implemented, stakeholders can check where the data comes from, how it was used and the derived results, which builds trust in the system. Modern healthcare analytics platforms provide transparency by offering clear visualizations of how data flows through AI decision-making processes.
2. Demonstrating Proven Results
The best case of trusting and accepting AI for healthcare comes from evidence of its positive results. Healthcare consumers start trusting AI when it repeatedly makes better diagnoses, prevents common mistakes and leads to better treatment results. Studies suggest that AI technology in healthcare can decrease diagnostic mistakes by 30%, demonstrating their value in healthcare. When successful cases are documented, healthcare professionals and patients who doubt AI are more likely to become its supporters when they see the results for themselves.
3. Addressing Bias and Ensuring Fairness
Bias concerns in AI are a real challenge that requires systematic approaches to resolution. Since AI picks up biases from their training set, it is important to collect data that represents the whole population to promote equality. By regularly auditing and detecting biases, we can make sure that healthcare AI applications provide equal treatment to all kinds of patients. This becomes especially critical during healthcare data migration, where historical data patterns may perpetuate existing inequities in AI system training.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Standards
Following the established healthcare regulations further builds trust in the AI implemented in various medical environments. Artificial intelligence solutions must comply with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR, showing that they prioritize patient safety and data protection. Independent assessments from third-party audits on accuracy, safety and fairness offer unbiased opinions that can instill trust among the stakeholders and regulatory bodies. HIPAA-compliant software development ensures that functions well while meeting rigorous privacy requirements.
5. Patient-centred Data Governance
A fundamental shift in the healthcare AI governance approach is involving patients in data oversight. When patients participate in decisions regarding their data usage, trust naturally develops. Patient engagement in AI governance processes creates transparency and shows respect for patient autonomy in healthcare technology decisions. This approach aligns with modern healthcare trends focusing on patient-centered care and shared decision-making, with advanced medical records management systems that give the patient control over their information.
Strategies to Enhance Trust Through Data
There are key data-driven strategies that healthcare organizations can implement to build trust in AI for healthcare applications.
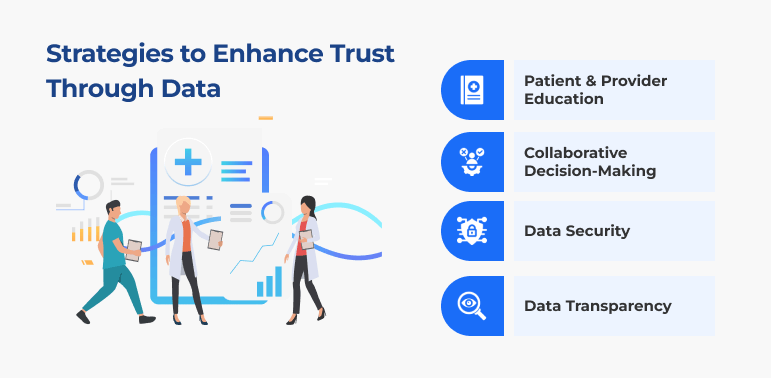
1. Patient and Provider Education:
Train them through programmes and resources. The training initiatives should be comprehensive and demystify the AI technology in healthcare and address specific concerns to gain confidence among patients and healthcare professionals.
2. Collaborative Decision-Making:
Incorporate patients in AI decision making. To ensure patient engagement, strategies regarding AI recommendation should be put in a clear manner to provide a meaningful opportunity for patients to participate in their treatment decisions.
3. Data Security:
Adopt strict data protection protocols and regulatory compliance. Organisations have to adopt HIPAA compliant software and put in place stringent security frameworks to safeguard the sensitive health information across all healthcare AI applications.
4. Data Transparency:
Ensure an effective transparency framework through documentation, tracking, explanations and verification. Transparency initiatives should not only cover diagnostic algorithms but also treatment recommendations, so that stakeholders know how decisions are made and validated.
Wrapping Up
Trust among patients and providers is needed to advance artificial intelligence in healthcare. AI systems are not replacement technologies, but collaborative partners. Effective utilization of strategic data that demonstrates transparency, fairness and measurable outcomes alleviates trust concerns.
To achieve AI and healthcare success, organizations must demonstrate how artificial intelligence can improve patient care while protecting privacy and engaging patients in governance. Clear communication, patient involvement, and robust data practices create the foundation for sustainable trust in healthcare technology.
The future of healthcare innovation depends on building confidence in AI in healthcare through evidence-based approaches that prioritize stakeholder needs.
The post AI in Healthcare: The Human Side of AI to Build Trust in Healthcare appeared first on Osplabs.





